In the dynamic world of financial markets, moving averages (MAs) serve as fundamental tools for traders, offering insights into market trends and aiding in the identification of potential entry and exit points. By smoothing out price data over a specified period, moving averages help distinguish between short-term fluctuations and the underlying market direction.
What is a Moving Average?
A moving average is a statistical calculation that analyzes data points by creating averages of different subsets of the full data set. In trading, it involves calculating the average of a security’s price over a specific number of periods, such as days or hours. This method helps in filtering out the “noise” from random price fluctuations, providing a clearer view of the market’s direction.
Types of Moving Averages
There are several types of moving averages, each with distinct characteristics:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): The SMA is calculated by adding the closing prices of a security over a set number of periods and then dividing by that number. For example, a 5-day SMA sums the closing prices of the last five days and divides by five. This method treats all data points equally, which can be beneficial for identifying longer-term trends.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): The EMA gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to new information. It is calculated using a smoothing factor that applies more significance to the most recent prices. This responsiveness can be advantageous in fast-moving markets like forex and cryptocurrency.
- Weighted Moving Average (WMA): The WMA assigns different weights to each data point, with more recent prices typically receiving higher weights. This approach allows traders to place more emphasis on recent price movements while still considering historical data.
Calculating Moving Averages
- Simple Moving Average (SMA) Formula:SMA = (P₁ + P₂ + … + Pₙ) / nWhere Pₙ represents the price at period n, and n is the number of periods.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA) Formula:EMA = (Pₙ × α) + (EMAₙ₋₁ × (1 – α))Where α is the smoothing factor, calculated as 2 / (n + 1), and EMAₙ₋₁ is the previous period’s EMA.
Moving Averages in Forex Trading
In the forex market, moving averages are extensively used to identify trends and potential reversal points. Traders often employ multiple moving averages with varying periods to gain a comprehensive view of market dynamics.
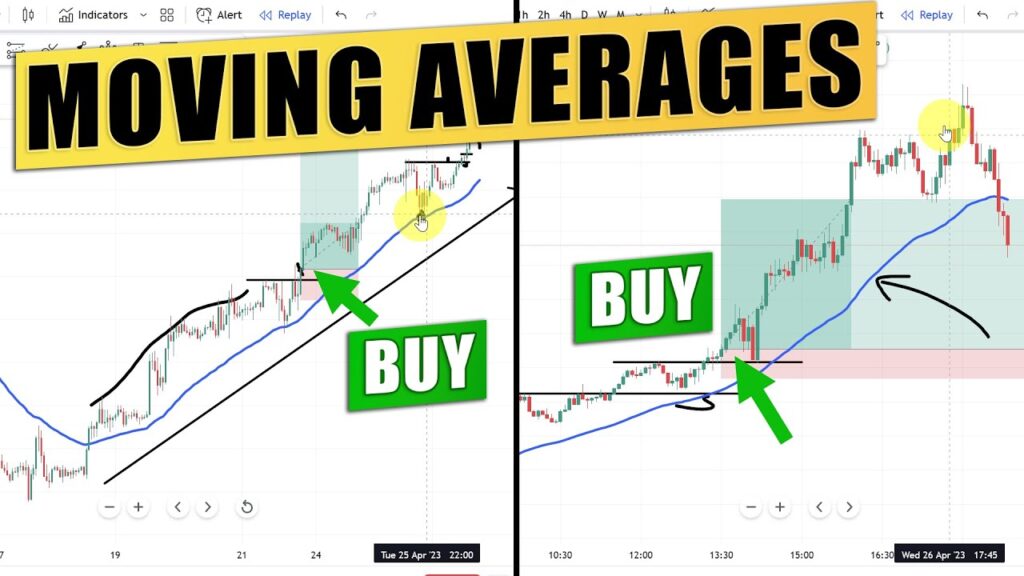
- Trend Identification: A rising moving average indicates an uptrend, while a declining moving average suggests a downtrend. Traders monitor the slope and direction of the moving average to assess market momentum.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Moving averages can act as dynamic support and resistance levels. For instance, a price bouncing off a moving average may indicate support, while a price failing to break above a moving average could signify resistance.
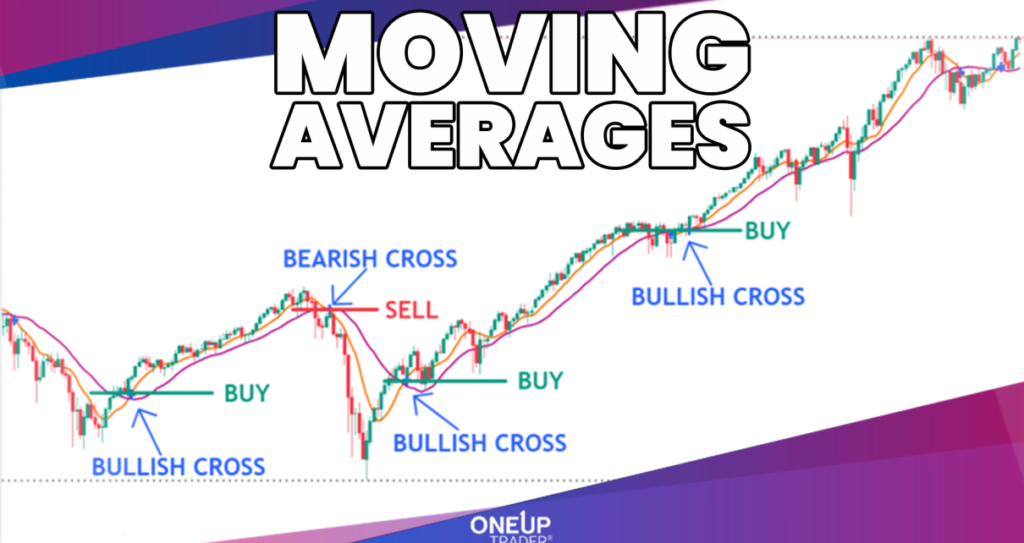
- Crossover Strategies: Traders often use crossovers between different moving averages as trading signals. For example, when a short-term moving average crosses above a long-term moving average, it may signal a buying opportunity, and vice versa for a selling opportunity.
Moving Averages in Cryptocurrency Trading
The cryptocurrency market, known for its volatility, also benefits from the application of moving averages. Given the market’s 24/7 nature, moving averages provide a consistent method for analyzing price trends.
- Trend Analysis: Similar to traditional markets, moving averages in crypto trading help in identifying the prevailing market trend, whether bullish or bearish.
- Volatility Smoothing: Cryptocurrencies often experience significant price swings. Moving averages help smooth out these fluctuations, allowing traders to focus on the broader market direction.
- Signal Generation: Crossovers and other moving average-based strategies are employed to generate trading signals, assisting traders in making informed decisions.
Practical Example: Applying Moving Averages
Consider a trader analyzing the EUR/USD currency pair using a 50-day SMA and a 200-day SMA.
- Bullish Signal: If the 50-day SMA crosses above the 200-day SMA, it may indicate a potential buying opportunity, suggesting a shift to an uptrend.
- Bearish Signal: Conversely, if the 50-day SMA crosses below the 200-day SMA, it could signal a selling opportunity, indicating a potential downtrend.
These crossovers are commonly referred to as “Golden Cross” (bullish) and “Death Cross” (bearish).

Conclusion
Moving averages are indispensable tools in both forex and cryptocurrency trading, offering clarity amidst market noise and assisting traders in making informed decisions. By understanding and applying various types of moving averages, traders can enhance their technical analysis and improve their trading strategies.